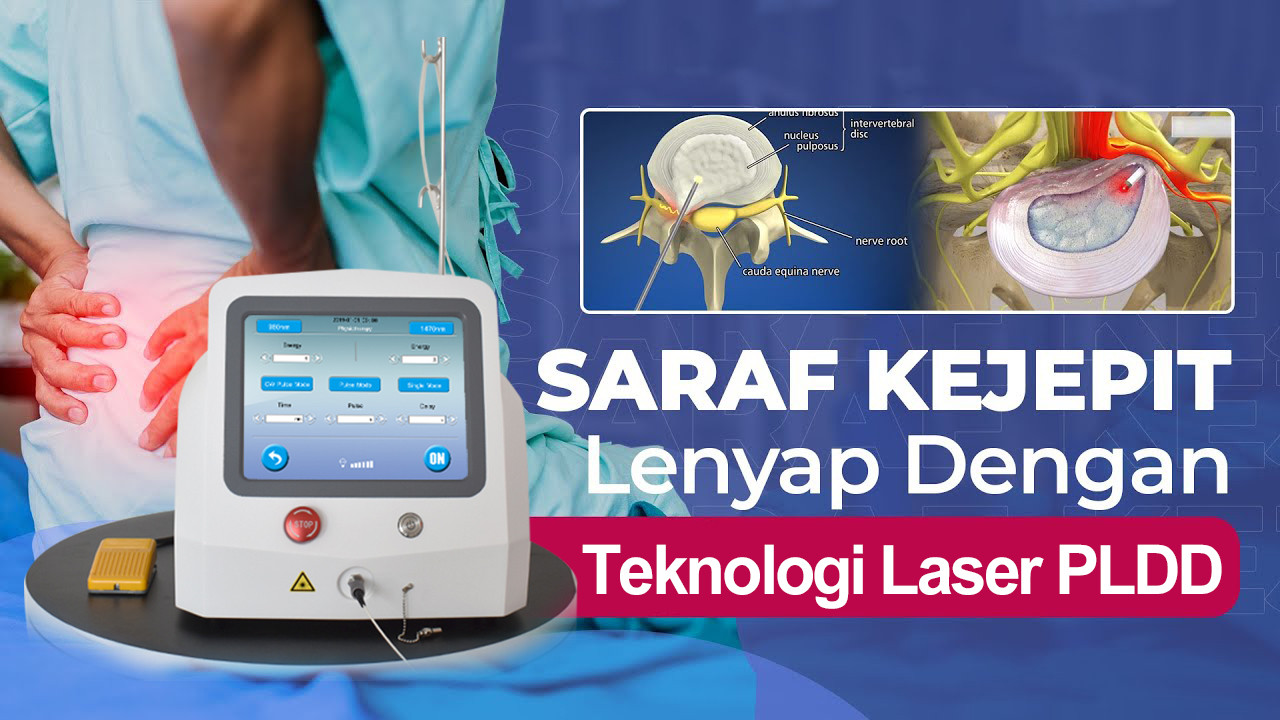
Background and objective: Percutaneous laser disc decompression (PLDD) is a procedure in which herniated intervertebral discs are treated by reduction of intradiscal pressure through laser energy. This is introduced by a needle inserted into the nucleus pulposus under local anesthesia and fluoroscopic monitoring.
What are the indications for PLDD?
The main indications for this procedure are:
- Back pain.
- Contained disc which is causing compression on nerve root.
- Failure of conservative treatment including physio and pain management.
- Annular tear.
- Sciatica.
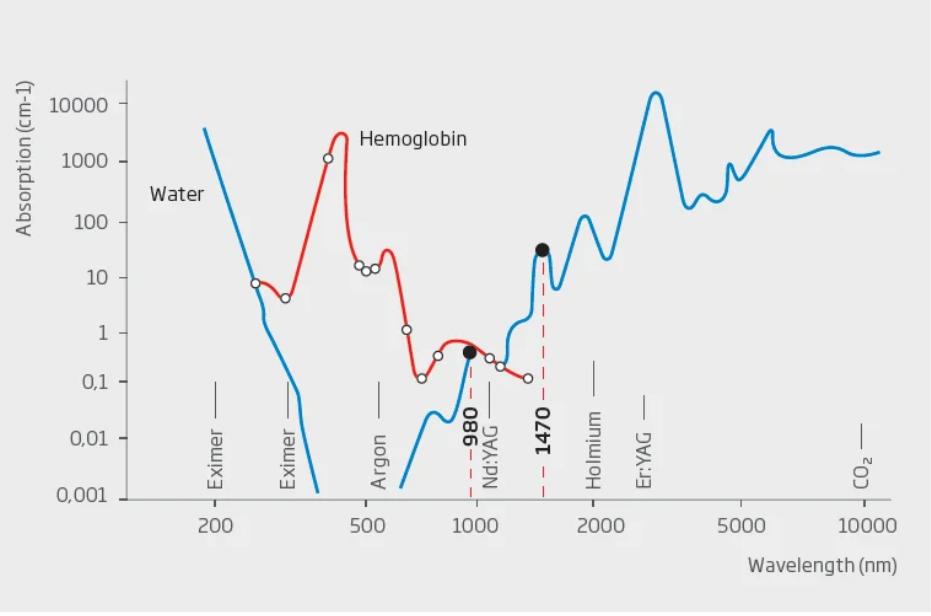
Why 980nm+1470nm?
1.Hemoglobin has a high absorption rate of 980 nm laser, and this feature can enhance hemostasis; thereby reducing fibrosis and vascular bleeding. This provides the benefits of postoperative comfort and a more rapid recovery . In addition, considerable tissue retraction, both immediate and delayed, is achieved by stimulating collagen formation.
2. The 1470nm has a higher water absorption rate, the laser energy to absorb the water within the herniated nucleuspulposus creating a decompression. Therefore, the combination of 980 + 1470 can not only achieve a good therapeutic effect, but also prevent tissue bleeding.
What’s the advantages of PLDD?
The advantages of the PLDD include being less invasive, shorter hospitalization and faster recovery compared to conventional surgery , Surgeons have recommended PLDD for patients with disk protrusion, and due to its advantages, patients are more willing to experience it
What is the recovery time for PLDD surgery?
How long does the recovery period last after the intervention? Following PLDD surgery, the patient can leave the hospital that day and is usually able to work within a week after a 24-hour bed rest. Patients who do manual labour can only return to work after 6 weeks after the full recovery.
Post time: Jan-31-2024